Papillomavirus (HPV, HPV-human papillomavirus) or papillomavirus is a group of infections that contains more than 100 types of viruses, 80 of which are pathogenic to humans. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, 70% of the world's population are carriers of HPV. In most cases, infection occurs after the onset of sexual activity and can be asymptomatic for a long time.
Causes of HPV infection
Symptoms of papillomavirus infection in women can include: various types of warts, flat and genital warts, cervical dysplasia. However, the most dangerous manifestation of the pathology is the development of cervical cancer. There are also data linking the development of cancer of the anus, external genitalia, vagina and infection with certain types of papillomavirus (HPV 16, 18, 45, 56 type).
Transportation routes:
- Sexual intercourse.Is the main route of transmission of papillomavirus infection in humans. The use of a condom during sexual intercourse significantly reduces the risk of infection with the human papillomavirus, but it does not provide a reliable guarantee that infection will not occur, as the virus particles are very small in size.
- Way of contact and home.The causes of infection are the use of common intimate hygiene products: towels, soap, use of public toilets, bathtubs.
- Natural birth.HPV can be transmitted to children who become infected when a baby passes through the birth canal of an infected woman.
The origin of this infection is cells in the skin and mucous membranes of the patient. In this case, you may not even know that it has become a carrier of the virus, as warts and papillomas can be microscopic in size and be invisible on visual inspection.
Proposed factors contributing to the development of a viral infection:
- onset of sexual activity at an early age;
- promiscuous sex without using a condom;
- frequent abortions;
- presence of infectious diseases of the genitals;
- long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- decreased body immune response;
- that the rules of personal hygiene are not followed;
- if your sexual partner has HPV;
- exposure to frequent stressors;
- bad habits.
Through pores, cracks, arms in the skin and mucous membranes, the virus enters the base of the epithelium, which ensures normal growth and regeneration of the skin and mucous membranes. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of basal cells carries information about the healthy structure of the cells. Viral particles, which are embedded in DNA, alter this information and cause the cells to be affected, which in the process of growth and disintegration cause the symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms of papillomavirus infection in women
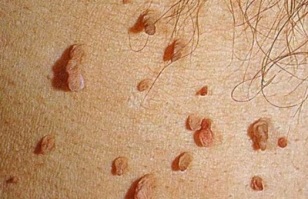
One of the possible manifestations of papillomavirus infection in humans is the appearance of genital warts and papillomas. They are special formations that look like cauliflower, grape bun or hanaham, pink-red or flesh-colored. Depending on the type and type of viruses, they can infect human skin and mucous membranes.
Genital warts can form around or near the anus, especially in the case of anal sex.
Papillomas can appear on the skin around the fingers, toes, hands, around the eyes, armpits and scalp. They also sometimes form on the soles of the feet and cause characteristic soreness when walking.
This type of disease rarely progresses to malignancies and cancers, but to prevent the development of the disease, surgery is removed by surgery.
Consequences of HPV infection
Human papillomavirus can lead to significant growth of genital warts, papillomas, flat warts, which cause discomfort, pain and when injured, bleeding of varying severity can occur.
Eighteenth- and sixteenth-type HPVs are the most dangerous, as they lead to the development of cancer. Cervical cancer, which has been reliably linked to papillomavirus infection in humans, ranks second among various malignancies in women. Its mortality rate reaches fifty percent.
Flat warts
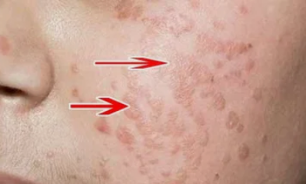
The disease is characterized by the formation of smooth plates that almost do not reach the skin.
Most often, vaginal and cervical mucosa is affected.
Their cosmetic defects are much smaller than genital warts.
This type of pathology has a higher risk of developing cancer.
Dysplasia of the cervical mucosa
Pathology is a change in the normal structure of cells in the lining of the cervix, called atypia. This condition in gynecological diseases is considered cancerous and requires examination and extensive treatment.
The disease is in most cases asymptomatic and is diagnosed by a standard examination by a gynecologist. Dysplasia of several stages of severity is distinguished: mild, moderate, severe. The choice of treatment method depends on the severity.
Cervical Cancer
This is the most dangerous manifestation of the disease. Cervical cancer ranks second in tumor pathology in women and is associated with HPV type 16, 18.
The disease may be asymptomatic or manifest as nonspecific symptoms: weakness, increased fatigue, weight loss, vaginal spotting outside the haemorrhage.
Disease Treatment Methods
If you have any signs of HPV infection, given the risk of consequences, do not seek medical attention yourself.
In order to select the best treatment technique, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist, who after thorough examination and the necessary research will prescribe adequate treatment.
To date, no drugs have been invented that cure HPV forever. The main goal of treatment is to reduce the concentration of the virus in the body to prevent further progression of the disease.
Main areas of treatment:
- manifestation of manifestations (warts, papillomas, dysplasia);
- antiviral therapy;
- use of funds aimed at enhancing immunity.
In the presence of papillomas, genital warts, warts, areas with dysplasia, even to a small extent, it is recommended to remove them, as the presence of tumors increases the concentration of viral particles in the woman's body which contributes to the further progression of the pathology.
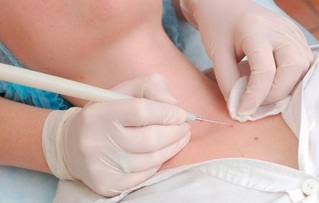
Surgery
The procedures for removing genital warts, papillomas, warts and dysplasia are as follows:
- surgery;
- mask treatment;
- diathermocoagulation;
- solvent solidification;
- radio wave therapy;
- chemical attack.
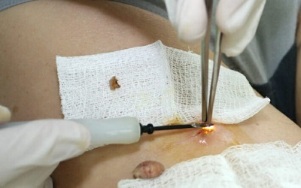
The surgical method involves removing the growth with a scalpel, it is the cheapest treatment method, although after it has a noticeable cosmetic defect and the healing time is significantly extended. There is also a risk of side effects. Therefore, this type of intervention is widely used.
During masking, liquid nitrogen is applied to the affected area, which freezes pathogenesis. After a few days, the papilloma or condyloma disappears and a small wound forms which heals in 10-14 days.
Diathermocoagulation is the application of high temperature to the area of the affected skin. This procedure is quite painful and therefore requires anesthesia. The disadvantage of this method is the formation of coarse scars instead of pathological images.
During solidification, the effects of the laser beam on the affected area lead to tumors drying out. Dry crust forms in its place, which after a while disappears without leaving a scar. This type of treatment is the mildest, but its high cost is considered a disadvantage.
Radiation therapy consists of exposing the affected area to radio waves. When using this type of treatment there is no risk of bleeding, no noticeable scars form, but the disadvantage is the high cost.
The chemical method is used when there is little formation. A special medicine is applied to the affected area. After a few applications, a crust forms on the treated area and disappears after a few days.
Drug use
Chemotherapy for human papillomavirus infection includes the following groups of drugs:
- antiviral drugs;
- immunostimulants.
To reduce the strength of the virus in a woman's body and prevent further reproduction, long-term antiviral therapy is recommended. The medicine is used in the form of tablets and plugs, the dose and duration of the treatment cycle should only be determined by your doctor.
Immunostimulants are prescribed after diagnosis and diagnosis of impaired immunity to increase the body's defenses, accelerate the appearance of immune cells and stimulate the formation of antibodies aimed at fighting the virus.
Treatment of HPV infection in pregnant women
The presence of papillomavirus infection in a woman's body does not affect the reproductive system and is not contraindicated in pregnancy. If HPV worsens during pregnancy, treatment for this condition is not performed during this period, postpartum treatment is prescribed.
But a woman must be under medical supervision throughout her pregnancy. With the development of severe discomfort, mild methods of treatment are prescribed. In extreme cases, when there are contraindications to the vagina due to the progression of HPV, a caesarean section is performed.
Getting Rid of HPV With National Remedies
At home, such folk remedies as herbal decoctions and infusions - for the treatment of papillomatosis, ointments - can be used to get rid of warts, papillomas and warts as a result.
Ways to prepare decoctions and infusions for the treatment of human papillomavirus infection:
- Horsetail, nettle herb, rose hips, dandelion roots, plantain leaves are mixed in equal amounts. In 3 pcs. l. Add 800 ml of water to the resulting mixture, boil for 10 minutes on low heat and then blow for 3 hours. Use 1 glass 3 times a day 30 minutes before a meal.
- Oregano herb, yarrow, immortal, St. John's wort, birch buds, nettles, petals, cauliflower, red-red, chamomile flowers, string, plantain leaves, celandine, linden, carcass, sage are mixed in equal amounts. Pour 2 tbsp into a thermos. l. the resulting mixture, pour 500 ml of boiling water, leave overnight. Take 0, 5 cups 4 times a day.
- Valerian root, lemon balm herb, oregano, fountain flowers, hop cones, motherwort are mixed in equal amounts. Pour 1 tbsp into a thermos. l. the resulting mixture, pour 0, 5 liters of boiling water and leave for 3-5 hours. Use 250 ml 2 times a day.
For spatial image handling, apply:
- Celandine safi. The juice is made from fresh leaves or bought at a pharmacy. Before applying the product, the skin must be evaporated on the affected area and a healthy area close to the affected area treated with a lotion. Celandine must be applied carefully to the affected skin. The procedure should be repeated every two days a week until the pathogenesis disappears.
- Garlic. The vegetables should be grated on a fine grater and mixed with the lotion until a viscous liquid is formed. Put the resulting mixture on the formation site for 2-3 hours every day for a month. After the operation, wash the skin with soapy water.
- Young walnuts. They must be crushed with a meat grinder, pour the resulting mixture into a 0, 5 liter glass jar to fill 2/3, pour the rest of the container with kerosene. Leave for 20 days and then strain through the cheesecloth. Infusion to treat the affected skin 2 times a day.
After treatment and relief of external symptoms of HPV, a woman needs to see a gynecologist every six months to monitor and prevent further progression of the disease.














































































